

- Razorsql 6.4.1 key serial key#
- Razorsql 6.4.1 key license key#
- Razorsql 6.4.1 key update#
- Razorsql 6.4.1 key password#
Razorsql 6.4.1 key update#

Razorsql 6.4.1 key serial key#
Main Features: Razorsql Serial Key Generator It can query, compare tables, import or export data, produce back-up of tables or a database that is entirely cut or merge files, obtain detailed information on the DB, appearance at logs and much more. RazorSQL Crack is well made, light and reacts quickly to commands. The work environment is very comprehensive but is intended limited to advanced level and users which are professional. It also includes a SQL script that is a compelling writer.
Razorsql 6.4.1 key license key#
RazorSQL License Key features a programming editor and boasts suitably of many languages that commonly used.
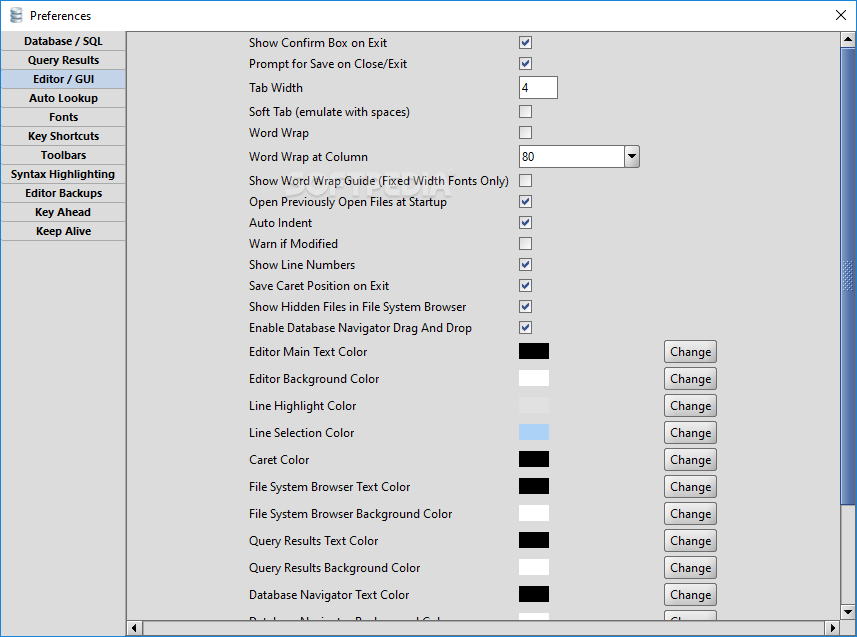
It supports tabs and gives you to open database that is multiple simultaneously. The following sections describe each of these authentication methods in more detail.RazorSQL Crack is a SQL that is the excellent query, database web browser, SQL editor, and database admin device. All the other options require some kind of external security infrastructure (usually an authentication server or a certificate authority for issuing SSL certificates), or are platform-specific.
Razorsql 6.4.1 key password#
Password authentication is the easiest choice for remote connections. Peer authentication is usually recommendable for local connections, though trust authentication might be sufficient in some circumstances. PAM authentication, which relies on a PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) library.īSD authentication, which relies on the BSD Authentication framework (currently available only on OpenBSD). RADIUS authentication, which relies on a RADIUS authentication server.Ĭertificate authentication, which requires an SSL connection and authenticates users by checking the SSL certificate they send. LDAP authentication, which relies on an LDAP authentication server. This is not supported for remote connections. Peer authentication, which relies on operating system facilities to identify the process at the other end of a local connection. (On local Unix-socket connections, this is treated as peer authentication.) Ident authentication, which relies on an “ Identification Protocol” ( RFC 1413) service on the client's machine. SSPI authentication, which uses a Windows-specific protocol similar to GSSAPI. Typically this is used to access an authentication server such as a Kerberos or Microsoft Active Directory server. GSSAPI authentication, which relies on a GSSAPI-compatible security library.

Password authentication, which requires that users send a password. Trust authentication, which simply trusts that users are who they say they are.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
